Knowing where an Emergency Dentist is located and having contact details will help in being prepared for dental emergencies. It can help to prevent unnecessary pain and potentially life threatening situations. Most Dental Surgeries will have an out of office hour contact for emergency treatment. Depending on the type of dental coverage certain emergency procedures such as an avulsed tooth (knocked out), abscess or hemorrhaging may be automatically covered. The need to act quickly is important for pain relief and to treat bacterial, fungal or virus infections.
Types of Dental Pain
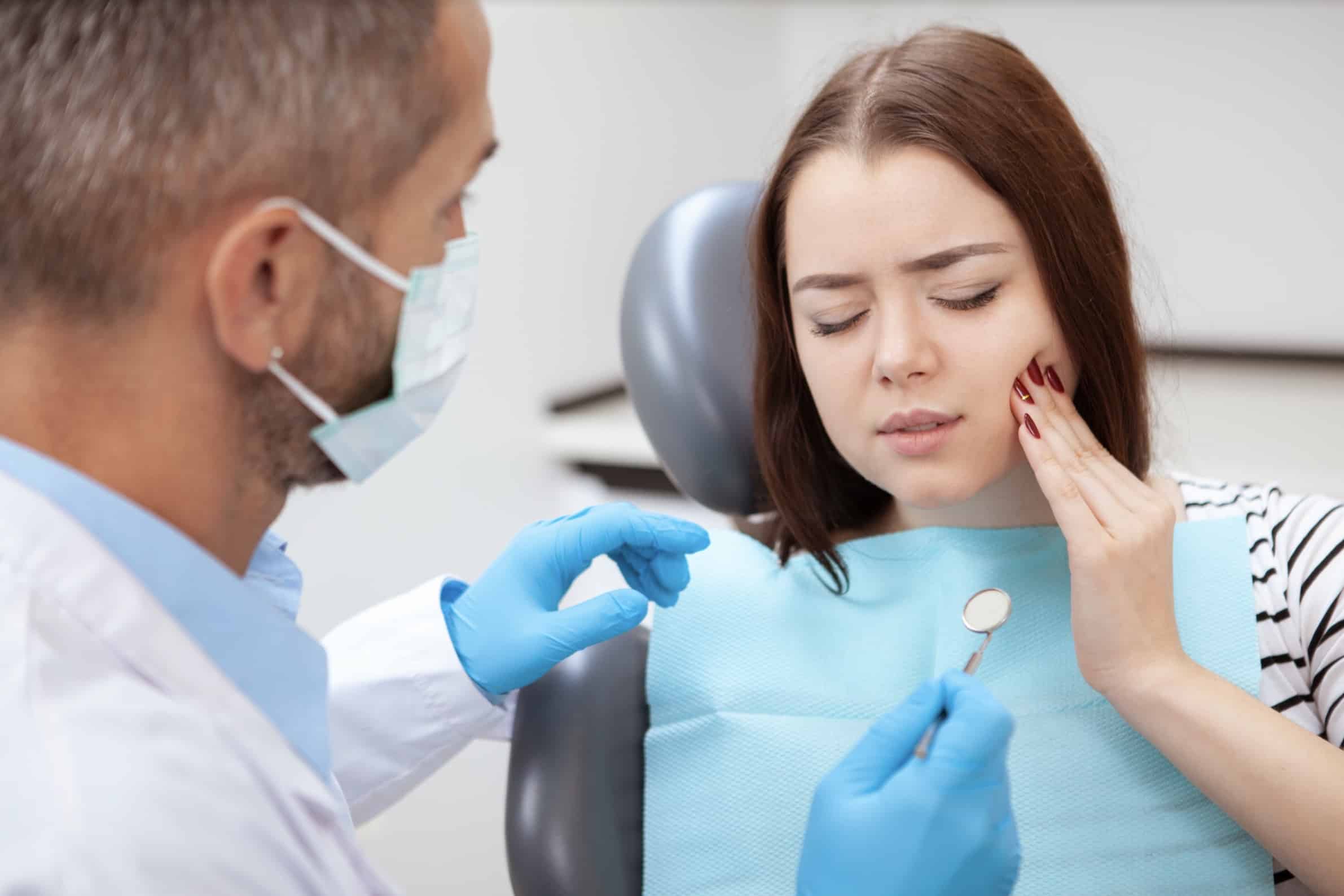
Odontogenic pain is tooth pain associated with the condition of the dental pulp of the teeth or the per-radicular tissues (at or near the root of the teeth). Orofacial pain is pain emanating from the face, jaw, or mouth. This type of pain may be caused by many conditions such as infections, an abscess, cysts, allergic reactions and salivary gland conditions. Having teeth sensitivity to cold (dentine hypersensitivity) may be mildly painful but usually indicates healthy dental pulp if there is no inflammation. Twenty percent of Americans have tooth sensitivity. Having a sharp pain to cold, hot, when the tooth is touch, eating something sweet and biting down can indicate reversible pulpitis. There may also be mild inflammation with this condition but no night time pain, or pain not associated with direct tooth contact. Most of the time teeth with this condition can be saved.
Irreversible pulpitis symptoms include running a fever, swollen lymph nodes and a bad taste in the mouth and bad breath. This type of dental damage is caused when the teeth enamel and dentin layers are damaged. An injury to the tooth, cavities, exposure of the tooth pulp from a fractured tooth or chronic conditions such as jaw misalignment and Bruxism (tooth grinding) can cause permanent damage.
Risk Factors for Tooth Pulpitis
Certain medical conditions such as Diabetes mellitus, (DM) a metabolic disease, can cause increase the risk of developing tooth pulpitis. A study published in the International Endodontic Journal in August 2013 states the because DM affects the ability for wound healing dental pulp integrity is compromised and there is also an increased incidence in perapical lesions which are caused by bacteria infections in the root canal system. DM also restricts dental collateral circulation and increases the chance of ischaemia which is necrosis (death of the cells) of the tooth pulp.
Not brushing teeth regularly, or for not a long enough time, two minutes is recommended by the American Dental Association (ADA) can cause tooth decay. Brushing teeth in the morning is also recommended to clear overnight plaque which hardens into tartar which is a tooth irritant and can lead to gum disease. Over brushing, more than twice a day or for longer than four minutes each time can also cause problems and wear down the enamel and expose the nerves in the dentin layer of the tooth. Daily flossing of teeth is also recommended. Eating sugary foods, especially drinking sugar pop drinks, and eating refined carbohydrates increase the risk of tooth decay.
Professional boxers and hockey players who may have routine blows to the teeth and chronic tooth grinding (Bruxism) also increases the risk of tooth decay. Bruxism can occur while you are awake (awake bruxism) or while sleeping (sleep bruxism). Risk factors for Bruxism are Stress and Anxiety as well as being angry. Bruxism is more common in children or in personality types that are hyperactive, or that are aggressive or competitive. Some antidepressants may also cause Bruxism as well habits like smoking, alcohol consumption and drinking drinks with caffeine or substance abuse. A family history of Bruxism also increases the risk factor, especially for Sleep Bruxism. Medical conditions such as Parkinson’s Disease, Dementia, Gastroesophageal Reflux Disorder, (GERD), sleep disorders like Sleep apnea or having Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) can have an increased risk factor for developing Bruxism. In extreme cases of Bruxism it may cause facial and jaw pain, damage the teeth, the jaw and dental work. Bruxism complications can also happen in the temporomandibular joints (TMJs) such as Trismus where muscle spasms prevent the mouth from opening.
Pulpitis Treatment
To determine if the tooth condition is pulpitis, the dentist will check for sensitivity to hot, cold, sweet and touch with a blunt dental tool or may use an electric pulp tester. If the electric charge can be felt the tooth pulp is still salvageable. A tooth x-ray may also be taken to see the extent of the tooth damage and the amount of inflammation. Reversible pulpitis can be treated by reducing the inflammation and by having the tooth cavity filled. These both help reduce the tooth pain.
For irreversible pulpitis the tooth pulp is dead and it may need to be removed by extraction. In some cases an Endodontist can perform a pulpectomy where the tooth pulp is taken out but the tooth itself is left. This is procedure is called a root canal. The tooth is then disinfected; the tooth is filled and then sealed. Antibiotics are given to prevent infections and painkillers are recommended or prescribed for after procedure healing time. For those with congenital heart condition antibiotics are prescribed before the dental procedure as an endocarditis prophylaxis. This prescription is given to prevent risk of contracting infective endocarditis. If after having a root canal or tooth removed the previous symptoms return or if the area becomes more painful or swelling occurs you should contact the dentist for follow up treatment.
Restorative Dental Emergencies
Restorative emergency dental work is another main cause of needing an Emergency Dentist. This can be damage to Dental work such as a lost or broken filling or a broken crown or dentures. Tooth implants that are damaged or loose tooth implants caused by infection or injury may also need to be repaired.
An Emergency Dentist service should be researched in the local area preferably before a Dental Emergency because dental problems can be very painful and potentially life threatening if infections are present.